Did you know that thousands of businesses are started in the United States every year? The country reported 20 million new business applications in 2024.
As an entrepreneur, one of the most important decisions you’ll make during a business startup is choosing your business structure. It will impact the management structure, tax implications, and other operational processes of your company.
Most business owners either choose to run a sole proprietorship or a Limited Liability Company (LLC). However, unless you are a tax expert or a lawyer, the differences between these two business entities can be difficult to understand in practical terms.
Let’s take a closer look at the differences between sole proprietorship vs. LLC to help you make the best choice for your needs.
Check out the infographic below for quick answers and find the detailed information below it.

Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC: The Basics
Before we examine the differences between sole proprietorship vs. LLC to help you choose the best entity for your business, let’s first understand each in detail.
What is a Sole Proprietorship?
In the simplest terms, a sole proprietorship is an unincorporated business owned by one person and is the simplest business structure to form.
Compared to other business formats, a sole proprietorship is the least expensive business entity to form.
By default, the individual who runs a business on their own is a sole proprietor. For example, if you run a retail business, freelance, or provide certain services online, you automatically become a sole proprietor, unless you have formed a separate legal entity.
It’s also easy to identify a sole proprietorship because the owner’s name is usually the name of the business. However, it can choose to operate under a brand name or trade name.
To do that, you will have to file for a DBA “Doing Business As” to operate your small business under a fictitious name.
That said, the main feature of sole proprietorships is that there is no legal separation between the owner and the business. This means that the business owner enjoys all the profits and is responsible for all the business’s debts.
As a sole proprietor, you can use your personal bank account to operate the business. However, we highly recommend having a separate bank account for your business to keep your business and personal finances separate.
If your motivation for starting a sole proprietorship is to enjoy all the profits, bear in mind that the losses are also on you. And if by any chance the business is not able to pay its debts, your personal assets can be auctioned to clear them.
Overall, a sole proprietorship is characterized by one man’s capital, minimal legal formalities, single ownership, unlimited liability, and no profit sharing:
Image via GovDocFiling
Also Read:
- Sole Proprietorship vs Partnership: How Are They Different?
- Sole Proprietorship vs S Corp: Pros & Cons of Each
Formation Process for a Sole Proprietorship
Regarding formation, a sole proprietorship is the easiest business entity to form.
Other than a business license from your state, you don’t need much to operate a sole proprietorship. But if you provide professional services like accounting, you may need to get the necessary professional licenses required in your industry.
Sole proprietorships are also popular with individuals that do contractual work such as personal trainers and consultants. Starting as a sole proprietor is the best way to go if you are not yet making a lot of money to justify the operational costs of an LLC.
Even if you have operated your business for a long time, a sole proprietorship may still be your best option depending on your business.
Advantages of a Sole Proprietorship
You’ll have the following advantages when you create a sole proprietorship:
- No paperwork unless you are filing for a DBA or need a specific professional license to operate your business.
- There are no annual filings with the state.
- Profits and losses go to the owner’s personal tax return.
- Quick and easy to form.
- The proprietor enjoys the tax benefits of being self-employed, such as deducting the expenses of using their car or home for business operations.
Disadvantages of a Sole Proprietorship
While it offers many advantages, keep the following drawbacks in mind when you start a sole proprietorship:
- You don’t have any liability protection against business debts and lawsuits. This means the business owner can be sued for the business’ commercial activities.
- It’s more difficult to raise capital for an unincorporated business like a sole proprietorship than for businesses with a more formal structure like an LLC or a corporation.
- This is because it is difficult to establish the credit of a sole proprietorship since most financial institutions view it as a “personal” loan.
- You’ll have a lower market credibility when you don’t operate under a trade name. However, you can fix this by registering a DBA.
What is an LLC (Limited Liability Company)?
An LLC is a business structure formed by filing legal paperwork with your state and local government. An LLC can be formed by one or several people, known as members.
When setting up an LLC, the owners decide the operation process, management structure, and tax treatment. The business and membership structure are captured in legal documents called articles of organization or LLC operating agreement.
Once formed, an LLC becomes a separate legal entity from the owners. And because of this, a creditor cannot go after the personal assets of the owner(s) when the business is sued or fails to pay its debts. Additionally, the bankruptcy of an LLC is also considered separate from the owners.
An LLC is an attractive option for an individual who wants to protect their personal assets. Those with employees are also shielded from the liability of their actions.
You can easily identify a business that has been registered as an LLC because its legal name ends with the abbreviation LLC or the phrase “Limited Liability Company.”
But similar to a sole proprietorship, an LLC can also register a DBA to operate under a different trade name.
By default, an LLC that’s owned by one person is taxed just as a sole-proprietorship. But it can also choose to be taxed as a C-corporation or an S-corporation.
This tax flexibility gives the owners the opportunity to choose the tax structure that’s the most cost-effective for their business. For most business owners, this is the main reason to set up their businesses as an LLC.
Image via GovDocFiling
Also Read:
- Freelance LLC Guide: Everything You Should Know
- Single-Member LLC vs. Multi-Member LLC: How to Choose
When to Form an LLC
Here are a few reasons to create an LLC instead of operating your business as a sole proprietorship:
- When you want to add another owner to the business in the future. This is easy with an LLC.
- When you want to protect your assets from legal and financial liability.
- When you want to take advantage of local, federal, and state taxes.
Advantages of an LLC
Here are the key advantages of forming an LLC:
- The owners have limited liability protection against lawsuits, business debts, and other obligations.
- Due to a formal business structure, LLCs are considered more credible than sole proprietorships.
- This makes it easier for the business to acquire equity and other types of business financing.
- Business owners also enjoy the benefits of being self-employed.
- It offers tax flexibility as LLCs can choose how they want to be taxed.
Disadvantages of an LLC
You’ll face the following drawbacks when you form an LLC.
- More paperwork is required than a sole proprietorship.
- You have to make annual state fillings and pay associated fees.
- The cost of filing tax returns is higher.
- LLCs pay additional taxes like unemployment tax and state business taxes.
Pro Tip: Choose the best states to form an LLC to get added advantages and tax benefits.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between LLC vs. Sole Proprietorship
As we have seen from the definitions of sole proprietorship vs. LLC, how you structure your business impacts everything from daily operations to taxes.
If you are just starting out and are not sure which structure is best for you, the following issues will help you choose between sole proprietorship vs. LLC.
Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC: Ownership
A Sole Proprietorship is owned and run by one person.
One or more people can start, own, and run an LLC. Owners of an LLC are called members and they can be individuals, other LLCs, and foreign entities. However, banks and insurance companies can’t be members of an LLC.
Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC: Startup Costs
Setting up a business involves more than just printing business cards and launching a business website. Depending on the business entity, you may have to hire an attorney to draft articles of organization, membership agreements, and more.
As the forms for creating a business become more complex, the startup costs associated with registering the business also increase.
As a business owner, you must decide how much you are willing to pay to set up your new business. You must also decide how long you’re willing to wait to get the business operational.
A sole proprietorship is quick and cheaper to set up because there are few registration forms to deal with.
To register a sole proprietorship in Texas, for example, you only have to complete an Assumed Name Certificate (Form 503) with the state, which costs $25.
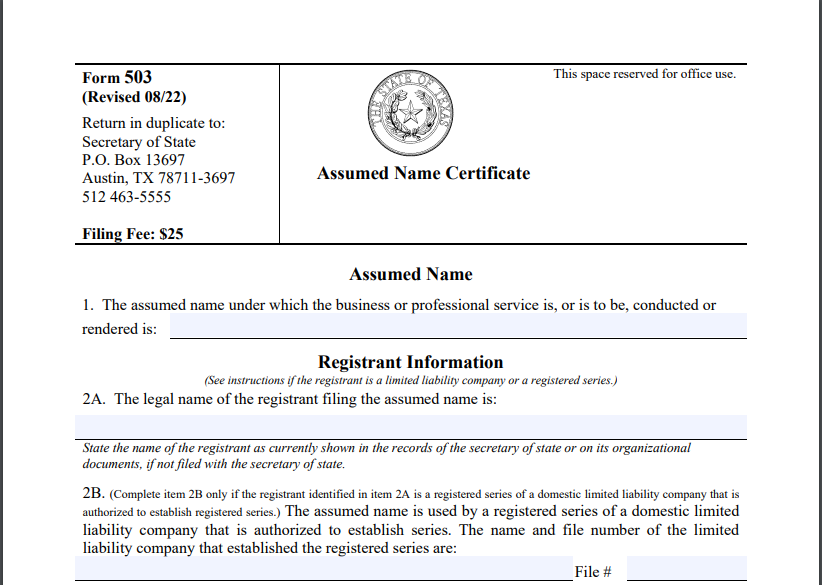
Image via Texas Secretary of State
On the other hand, an LLC takes longer to create because of the complex legal requirements. As an example, here’s how to start an LLC in Texas:
- Name your LLC: Choose a suitable name for your business. Ensure the name ends with the abbreviation “LLC” or the phrase “Limited Liability Company” as per Texas naming rights. Search your name to ensure it hasn’t been claimed by another organization.
- Choose a registered agent: The registered agent receives legal forms, government correspondence, and tax documents for your company.
- File the Certificate of Incorporation: Complete and file the Certificate of Incorporation with the state. Pay the $300 filing fee.
- Get an EIN: Get your Employer Identifier Number from the IRS for tax reporting.
Additionally, you may have to pay a franchise tax of between $800 and $1,000 to operate your business in some states.
All these fees raise the cost of starting an LLC. If you’re not willing to invest such amounts to get your business up and running, you better start with the cheaper sole proprietorship option.
Also Read:
- Steps to Starting A Business in Virginia
- Starting a Consulting Business Checklist: Everything You Need to Know
Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC: Formation Process
You may be surprised to learn that you don’t necessarily have to do anything to establish a sole proprietorship. In fact, you could be operating one right now without even knowing.
Anyone who provides services or sells goods is by default, a sole proprietor. For example, if you have a small garden and sell fruits and vegetables to your neighbors, you are automatically a sole proprietor even if you’re not registered with the state.
However, you need to formally register your business with the state to operate your business legally.
A Sole Proprietorship is easy to set up with no additional formation requirements if the owner operates the business under their own name. To run a business under a fictitious company name, you will need to file for a DBA (Doing Business As) in your state and pay a filing fee.
Depending on the nature of your business and the services you provide, you may have to acquire certain licenses, zoning clearances, and other permits to operate your business in your state.
The costs vary from state to state and you will have to check with your local government to find out how much you need to pay to get the necessary approvals.
For example, other than the business license for your sole proprietorship, you need at least 3 more licenses and permits to operate a food business in Arizona. These include:
-
- Certificate of occupancy: It shows that your business premises have been zoned out for running a food business. It also shows that it is up to date with the necessary checks and inspections.
- Food handler’s license: It allows you to sell and serve food to customers onsite. The license ensures that your restaurant employees know how to keep the restaurant safe from foodborne diseases.
- Food seller’s permit: You need a food seller’s permit if you sell tangible food products that attract a sales tax. With this permit, you can charge a sales tax on your food products.
- Liquor license: If you sell or serve alcohol to patrons, you will have to acquire a liquor license. The cost of a liquor license ranges from $2,000 to $5,000 depending on the liquor you serve.
Also, it requires more effort to form an LLC.
Forming an LLC requires that you file Articles of Organization with the Secretary of State. But before that, you will have to choose a name for your business. Search your proposed name before filing to ensure no one else is using the name.
You will also need to create an LLC Operating Agreement to define the roles and responsibilities of each member and manager (if any).
Next, you’ll have to choose a registered agent for the business. A Registered agent is a company or person who will receive government correspondence and tax documents for your company.
You can act yourself as the registered agent if you operate a single-person LLC or one of the members of your business in case your LLC has several members.
Alternatively, you can choose an entity to be your registered agent. However, the entity must be allowed to operate in the state your business is registered.
Lastly, you will need to pay a state filing fee that varies between $50-$500 across states. As an LLC owner, you will also have to pay ongoing annual filing fees in most states.
Before starting your LLC, check with the local authorities to see if you need to acquire other licenses or permits to operate the business.

Image via QuickBooks
Also Read:
- Business Startup Checklist: What New Businesses Need
- S-Corp Checklist: Essential Steps to Set Up Your Business
Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC: Operations & Management
A sole proprietorship is simple to operate because there’s only one person at the top. The owner can make any decision they deem fit for the business without checking with anyone.
The sole proprietor can hire employees to perform certain duties or hire consultants for legal services or bookkeeping but, at the end of the day, they are solely responsible for all business actions.
The sole proprietor must ensure the business is in compliance with regulations, and it’s generating enough profits to meet its financial obligations.
An LLC, on the other hand, has a little more complex operational and management structure. The operating structure is typically outlined in the LLC operating agreement, which clearly mentions:
- Each member’s share in the business
- Each member’s voting rights
- How the business profits will be shared
The members of an LLC can choose to collectively manage the company or hire a manager.
When it comes to decision-making, the issues of an LLC are decided based on each member’s stake in the business. For example, an owner with a 25% ownership in the business has one-quarter vote, and a member with 33% stake in the business has one-third vote.
The profits the business makes are also shared in line with the ownership stakes. In the example above, the 25% owner will receive a quarter of the business profits and the 33% owner will receive a third of the profits.
Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC: Tax Implications
Taxes play a key role when choosing between a sole proprietorship vs. LLC. Both structures allow for pass-through taxation, but their differences can significantly impact your financial obligations.
In a Sole Proprietorship, pass-through taxation requires you to report your business income on your personal income tax return. As the owner, you’ll use Form 1040 along with Schedule C for this.
A limited liability company also offers pass-through taxation, which means that the profits and losses of your company will pass through to the personal tax returns of each member.
Sole proprietorship vs. LLC also needs to pay a self-employment tax (Social Security and Medicare taxes), which is 15.3% of your net earnings. However, the difference is that a limited liability company (LLC) can choose to pay taxes as a C-corporation or an S-Corporation.
As an S-corp, the owners of the limited liability company become employees of the business. So, when the business pays them a salary, they all pay self-employment tax on the amount received. However, the rest of the business profits are distributed as dividends, which aren’t subject to self-employment tax.
Whereas, if a limited liability company elects to pay taxes as a C-corporation, the business is taxed separately from its owners. The Corporation pays corporate taxes on its profits, and then any dividends distributed to owners are taxed again. Additionally, owners will only pay self-employment taxes if they earn salaries from the business.
Other than income taxes, both sole proprietorship vs. LLC may need to pay other additional taxes. It doesn’t matter which business structure you adopt, you have to pay state business taxes and payroll taxes if you have employees.
You also need to charge and collect local sales taxes if you deal in taxable goods or services. The state of incorporation may also impose franchise taxes for a single-member LLC and other types of LLCs.
Image via GovDocFiling
Whether you choose sole proprietorship vs. LLC, understanding how your business structure affects tax obligations is essential for maximizing profits and staying compliant.
Also Read:
- What Is a Tax ID? Entrepreneur’s Guide to Employer’s Tax ID
- How to Change an LLC to an S-Corp in Simple Steps
Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC: Legal Protection
A sole proprietorship is an unincorporated business with no legal separation between the sole owner and the business. As such, the business owner is personally liable for the business’s debts.
When the business becomes bankrupt and can no longer pay its debts, the owner will file for bankruptcy. In this case, both personal and business debts will feature in the proceedings, putting the owner’s personal assets at risk.
Additionally, anyone who sues a sole proprietorship can name the sole proprietor in the lawsuit and go after their personal accounts or significant personal assets to settle claims. Unlike a separate legal entity like a limited liability company (LLC), a sole proprietorship provides no personal liability protection, leaving the owner exposed to risks.
A sole proprietor in a high-risk industry, like food service or construction, is particularly vulnerable. Even a minor oversight may lead to catastrophic financial consequences.
On the other hand, a limited liability company (LLC) has more legal protection for business owners. This is because an LLC is a legal business entity separate from the owners. The owners are not legally liable for the business obligations and their assets cannot be used to settle business debts.
When it gets to a point where the business can no longer continue operation because of massive debt, the business owners can file for business bankruptcy and not have to pay creditors from their own pocket. Only the company’s assets are liquidated to pay creditors, leaving the owners’ personal assets untouched.
Also, when someone sues an LLC, they cannot personally go after the owners. The owners will be held personally liable for fraud and other business malpractices but cannot be sued when the business fails to meet its obligations.
It’s crucial to maintain proper compliance by keeping business and personal accounts separate and following the LLC’s operating agreement. Failing to do so can result in piercing the corporate veil, which removes the personal liability shield.
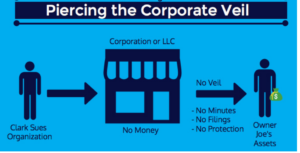
Image via GovDocFiling
Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC: Paperwork & Compliance
The other difference between sole proprietorship vs. LLC is related to business paperwork and compliance. As we’ve already mentioned, a sole proprietorship has the least paperwork requirements.
It only has to keep up with local, state, and federal taxes. A sole proprietor may also need to pay for the renewal of relevant business permits and licenses.
LLCs deal with more paperwork and have more compliance requirements than sole proprietorships. They are required to file annual reports in many states.
LLCs with many members have more responsibilities such as issuing membership units, developing an agreement, and holding regular member meetings.
The law doesn’t require an LLC to perform any of these steps but they are recommended for an LLC to operate optimally.
Lastly, due to it being an incorporated business entity, it requires more paperwork to dissolve an LLC.
Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC: Hiring Employees
Whether you operate a sole proprietorship or have registered an LLC, the employee compensation requirements are probably the same. Most states require businesses with employees to provide workers’ compensation.
Some states even have specific requirements regarding coverage for the sole business owner.
That said, if you decide to hire employees, it’s ideal to register your business as an LLC for liability purposes. This is because a limited liability company protects its owners from any wrongdoing by the employees.
If the business is found liable for negligence by one or several of its employees, the business assets can be seized. However, the owners of the LLC would not be held liable for the business debt and their assets will be protected.
All of the business’ assets are acquired and used to pay the settlement awarded to the pedestrian’s family. However, the personal assets of the owners cannot be taken and used to pay the settlement since they are not personally liable for the actions of the employees.
But if Paulman Bakery was a sole proprietorship, the personal assets of the owner can be taken to settle the award since there is no legal separation between the business and the owner.
Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC: Credit & Loans
If your business needs a line of credit to settle business overhead or a loan to acquire more assets, it’s less risky and more credible for a lender to finance an LLC than a sole proprietorship.
When push comes to shove an LLC can give ownership in the business as collateral in exchange for business financing. The owner of a sole proprietorship cannot do this because the entity can only have one owner.
To access a business loan, you’ll need at least a collateral, a business plan, and a personal credit score.

Image via Faster Capital
Also Read:
How to Choose Between a Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC
Choosing between a sole proprietorship vs. LLC depends on your business’s unique needs and goals. Use this guide below to evaluate your situation.
Assess Your Personal Assets
Evaluating your personal assets is one of the most crucial factors in selecting between sole proprietorship vs. LLC. Take inventory of what you own and what could be at risk in a lawsuit. This includes:
- Vehicles and valuable personal property
- Savings and emergency funds
- Retirement accounts
- Investment portfolio
- Home equity
- Expected inheritances or future assets
If you have significant personal assets, an LLC provides legal protections if your business faces legal troubles or can’t pay its debt.
While small business owners with limited assets may opt for a sole proprietorship, those with significant wealth should consider forming an LLC.
Evaluate Business Risk
Before choosing sole proprietorship vs. LLC, reflect on the nature of your business. Ask yourself the following questions:
- Will you provide professional services where mistakes can be costly?
- Will you sell products that can potentially harm customers?
- Is the industry highly regulated?
- Will you be signing contracts or taking on significant business loans?
If you answered yes to most of the questions above, a limited liability company (LLC) will be more suitable.
High-risk businesses, such as medical, cosmetics, and food services, are better suited for the legal protection an LLC offers. Conversely, low-risk businesses like freelancing writing can operate safely as a sole proprietorship because they have minimal liability risks.
Analyze Tax Preferences
Although both sole proprietorship vs. LLC offer pass-through taxation, a limited liability company offers more flexibility. A sole proprietor reports business income on Schedule C of their personal tax return. While this is straightforward, it lacks flexibility.
On the contrary, a limited liability company (LLC) can choose to be taxed as a sole proprietorship, S-corporation, or C-corporation. If you expect higher profits, opting for S-corp taxation can provide significant tax savings, potentially saving you thousands of dollars.
Think About Growth Plans
Your business structure should align with your long-term plans when choosing between sole proprietorship vs. LLC. If you plan to remain small and independent, a sole proprietorship offers simplicity.
An LLC offers more flexibility and better options If you plan to scale your business, hire employees, or attract investors. It makes it easier to do the following:
- Create a professional image
- Secure business loans
- Build business credit
Budget for Costs
Whether you’re settling for LLC vs. sole proprietorship, examine your current finances and future goals. For many small business owners on a tight budget, sole proprietorship offers the lowest initial costs.
You’ll avoid LLC filing fees, registered agents, and annual compliance fees. However, if you’re investing significant personal funds or taking loans, an LLC’s liability protection covers you as a separate business entity.
Research Industry Standards
Your business may fall within an industry with strict regulations. For instance, licensed professionals like lawyers, architects, and chiropractors are required to form a professional limited liability company (PLLC). Similarly, real estate investors often create multiple LLCs for each property to limit risk exposure.
For industries that require formal registration and business insurance to meet licensing or regulatory standards, an LLC is often the best choice. However, professionals and consultants in low-risk businesses may find sole proprietorship sufficient.
Consider Your Availability and Management Complexity
Your ability to manage administrative tasks plays a key role when choosing between a sole proprietorship vs. LLC.
A sole proprietor has minimal paperwork, and it’s limited to filing personal income tax returns. In contrast, an LLC has more requirements, including:
- Annual state filings
- More detailed records
- Separate business bank accounts
- Operating agreements
- Regular member meetings (for multi-member LLCs)
If you lack time for administrative tasks and can’t hire a professional, starting as a sole proprietor may be more practical.
In contrast, a sole proprietor must be actively involved in running the business. However, an LLC member doesn’t need to be an employee, allowing them to hire someone to manage the business in their absence.
Also Read:
- Low-Risk Business Ideas to Start Your Own Venture
- Important Legal Requirements for Starting a Small Business
Who Should Choose a Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC?
Deciding between a sole proprietorship vs. LLC depends on your business needs. Here’s a guide to help you determine which structure is best for you.
Who Should Choose a Sole Proprietorship?
A sole proprietorship is best suited for:
- Low-risk businesses, such as freelancers, consultants, and small businesses
- Entrepreneurs with minimal personal assets and limited exposure to lawsuits or liabilities
- Business owners looking for a simple and low-cost business structure with minimal administrative requirements
- Professionals who want to be the only owner to control directly all aspects of the business with no plans of expanding significantly in the future
Who Should Choose a Limited Liability Company (LLC)?
An LLC is ideal for:
- Entrepreneurs with significant personal assets to protect, such as home equity, savings, or investments
- High-risk businesses in industries like construction, manufacturing, or healthcare, where liability risks are high
- Business owners planning to scale, hire employees, or seek investors, as LLCs offer more professional credibility and flexibility
- Owners seeking tax flexibility, especially those anticipating high profits or planning to elect S-corp status to save on self-employment taxes
- Professionals in industries requiring formal registration or licensing, such as real estate investors and architects
Also Read:
FAQs
1. Which is better: sole proprietorship vs. LLC?
A. A sole proprietorship is easier to form and manage than an LLC. Its startup costs are lower than an LLC which charges about $300 to file the articles of association. However, unlike an LLC, a sole proprietorship doesn’t provide personal liability protection. This means the owner’s personal assets can be claimed to settle business debts.
The choice between these two business structures will depend on your personal preferences and business needs. If you want a cheap and easy startup process, go for a sole proprietorship. But if you want liability protection, register an LLC.
2. Which one is better for taxes, sole proprietorship or LLC?
A. Both sole proprietorships and LLCs pass through the business tax to the tax returns of the owners. However, an LLC has more tax flexibility because they can also choose for their business to be taxed as an S-Corp or a C-Corp.
3. Is a single member LLC the same as a sole proprietorship?
A. No, it isn’t. The only thing that makes single-member LLCs similar to sole proprietorships is how they are taxed. Both these entities pass their taxes to the business owner who reports the business income in their personal tax form.
Other than that, a sole proprietor cannot enjoy personal liability protection like the owner of a single-member LLC.
4. What are the advantages of a sole proprietorship?
A. A sole proprietorship is the simplest business entity to form. You’ll have the following advantages when you create a sole proprietorship:
- No required paperwork unless you are filing a DBA or need a specific professional license to operate your business.
- There are no annual filings with the state.
- Profits and losses are passed through to the owner’s taxes.
5. What are the advantages of an LLC?
A. Here are some of the advantages of an LLC:
- The owners have limited liability protection against lawsuits, business debts, and other obligations.
- Due to a formal business structure, LLCs are considered more credible than sole proprietorships.
- This makes it easier for the business to acquire equity and other types of business financing.
- Business owners also enjoy the benefits of being self-employed.
- It offers tax flexibility as LLCs can choose how they want to be taxed.
Also Read:
- How to Start Your Own Roofing Business: An Effective Guide
- How to Start a Virtual Bookkeeping Business
Wrapping Up
Regardless if you choose between sole proprietorship vs. LLC, make sure that you complete all legal requirements and paperwork correctly.
To simplify the process for you, we offer one, simplified online application for both state and federal filings. You can take advantage of our secure and cost-effective filing services to launch your new business.
Want to learn more about the key differences between a Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC? Check out the infographic below by GovDocFiling. It will also help you make an informed choice when it comes to choosing a business structure for your new business.

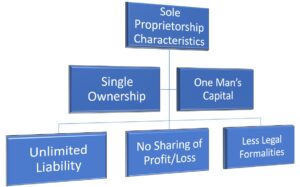
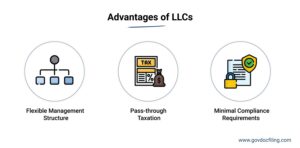
 Image via
Image via 